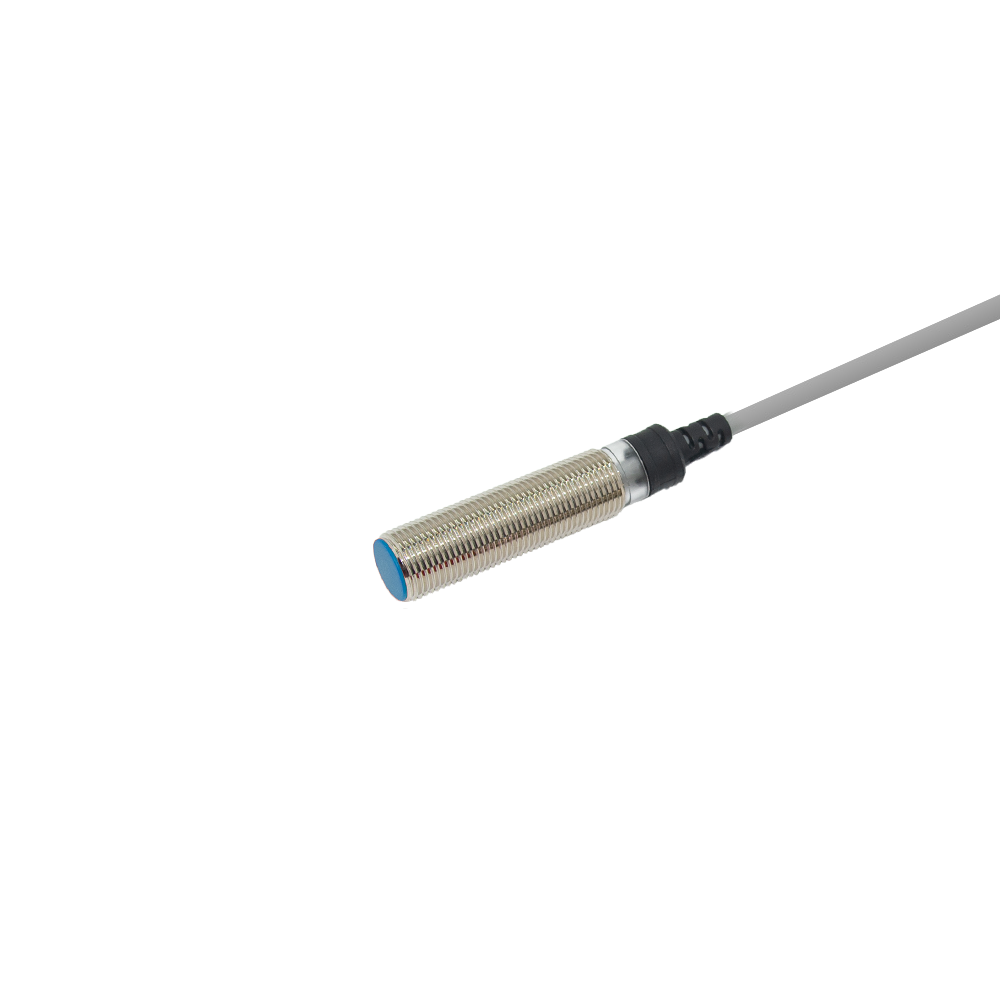
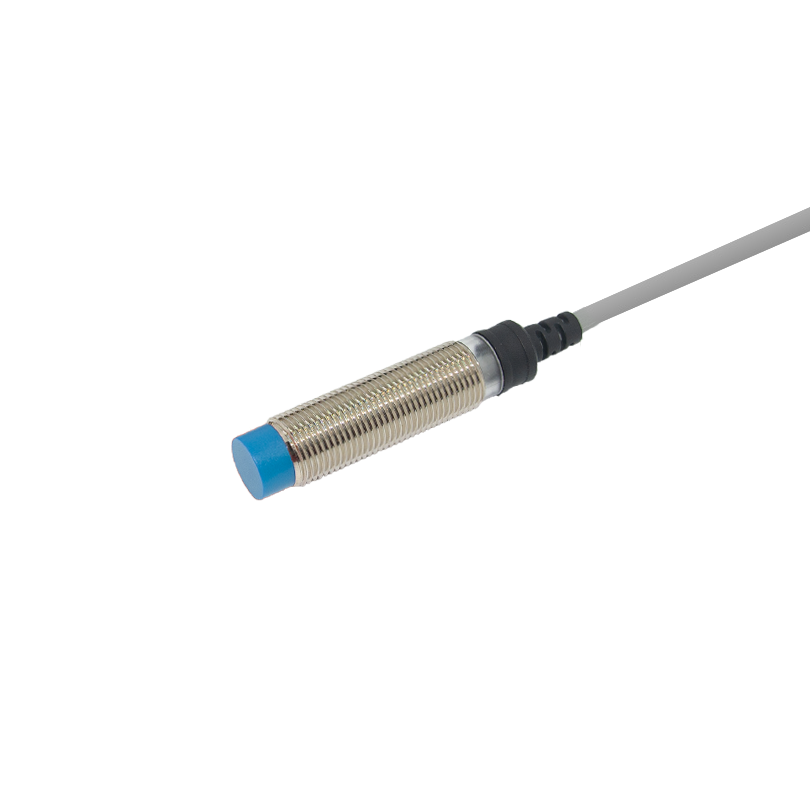
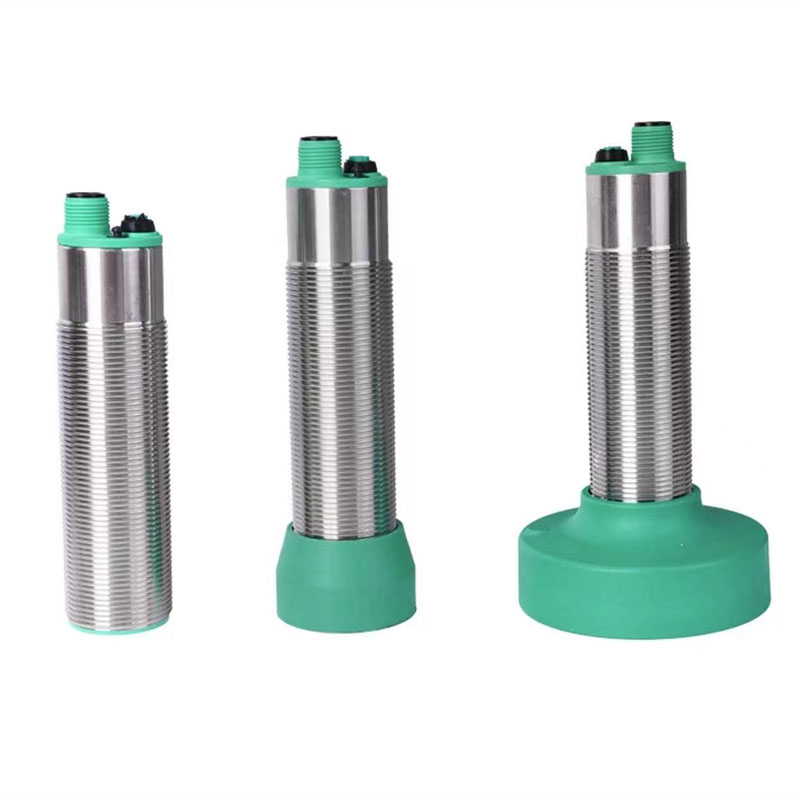
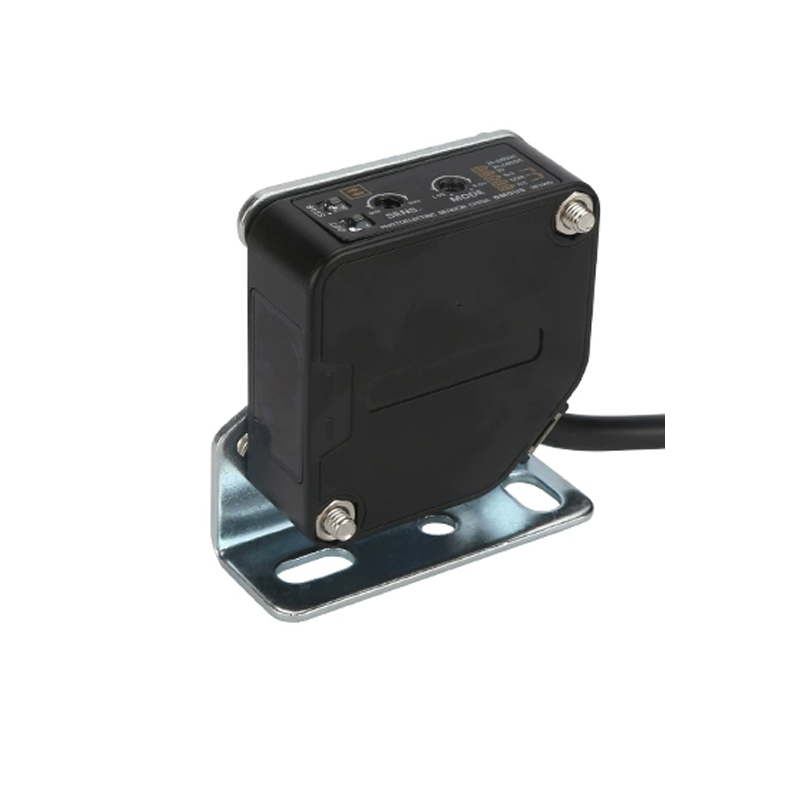
proximity sensor pnp and npn
Proximity sensors PNP and NPN are essential electronic devices that detect the presence of objects without physical contact. These sensors utilize different transistor configurations to achieve their sensing capabilities. PNP sensors use positive switching logic, while NPN sensors employ negative switching logic. Both types operate through electromagnetic fields, producing either a normally open or normally closed output signal when an object enters their sensing range. The key distinction lies in their current flow direction: PNP sensors source current to the load, while NPN sensors sink current from the load. These sensors find widespread application in industrial automation, manufacturing processes, and quality control systems. They excel in environments where mechanical switches would be impractical or unreliable. With sensing ranges typically from 1mm to 50mm, these devices can detect various materials, including metals, plastics, and liquids. The choice between PNP and NPN largely depends on the control system requirements and regional preferences, with PNP being more common in Europe and NPN in Asia. Their robust construction ensures reliable operation in harsh industrial environments, offering protection against dust, moisture, and electromagnetic interference.