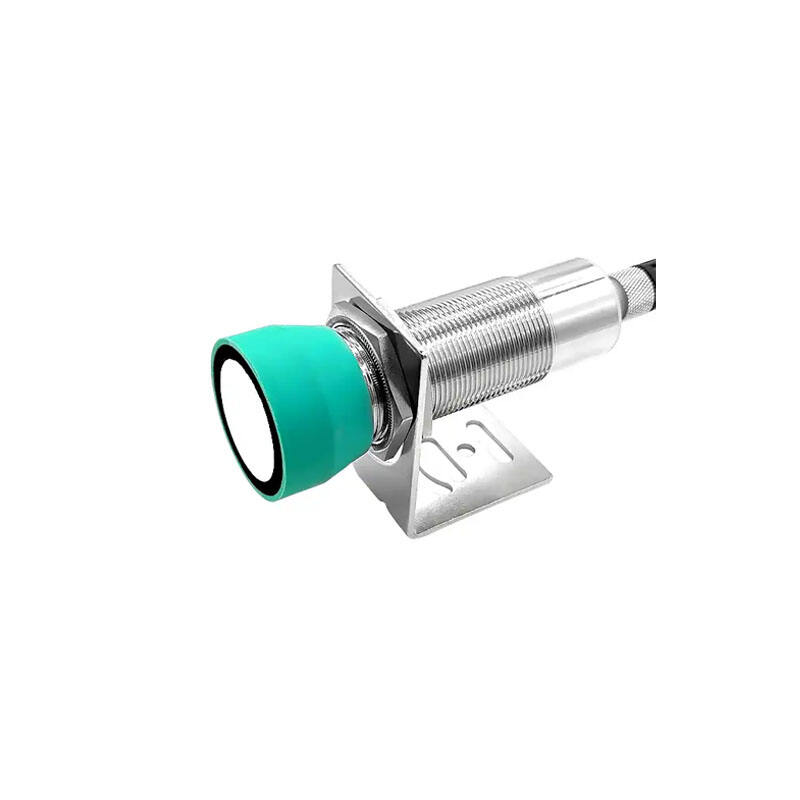
inductive sensor
An inductive sensor is a sophisticated electronic device that operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction to detect the presence or proximity of metallic objects. These sensors generate an electromagnetic field and monitor changes in that field caused by nearby conductive materials. When a metallic object enters the sensor's detection zone, it induces eddy currents in the target, causing a change in the electromagnetic field. This change is then converted into an electrical signal, allowing the sensor to determine the presence and often the distance of the metallic object. Inductive sensors are particularly valued for their robust construction, making them highly resistant to environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and temperature variations. They offer non-contact detection capabilities, which eliminates mechanical wear and extends their operational lifespan. These sensors are available in various sizes and configurations, with detection ranges typically spanning from a few millimeters to several centimeters. They operate with remarkable precision and can achieve rapid response times, making them ideal for high-speed applications. In industrial settings, inductive sensors play crucial roles in automation systems, position detection, counting applications, and quality control processes.