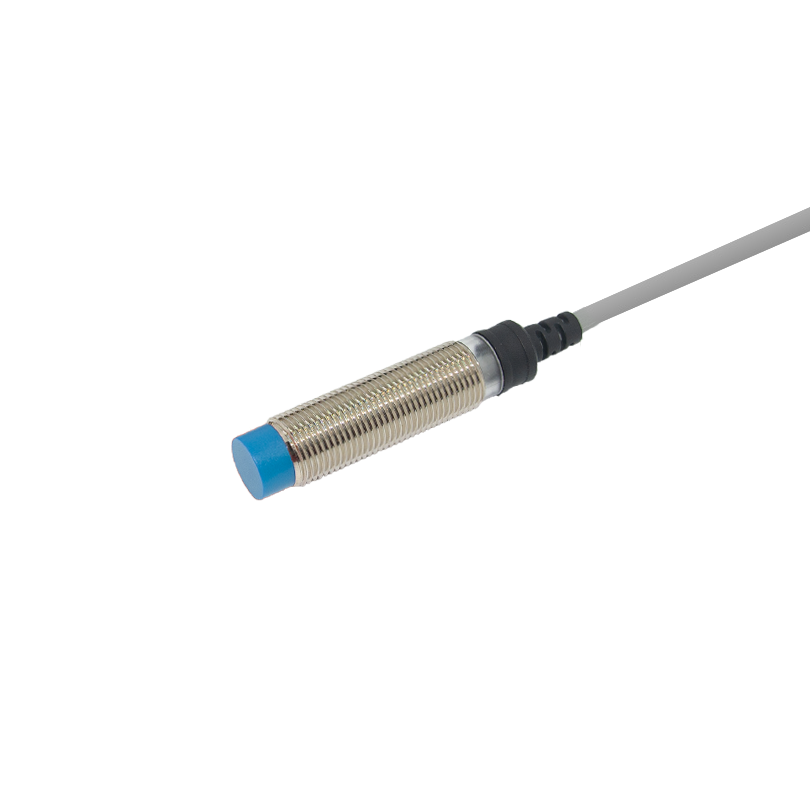
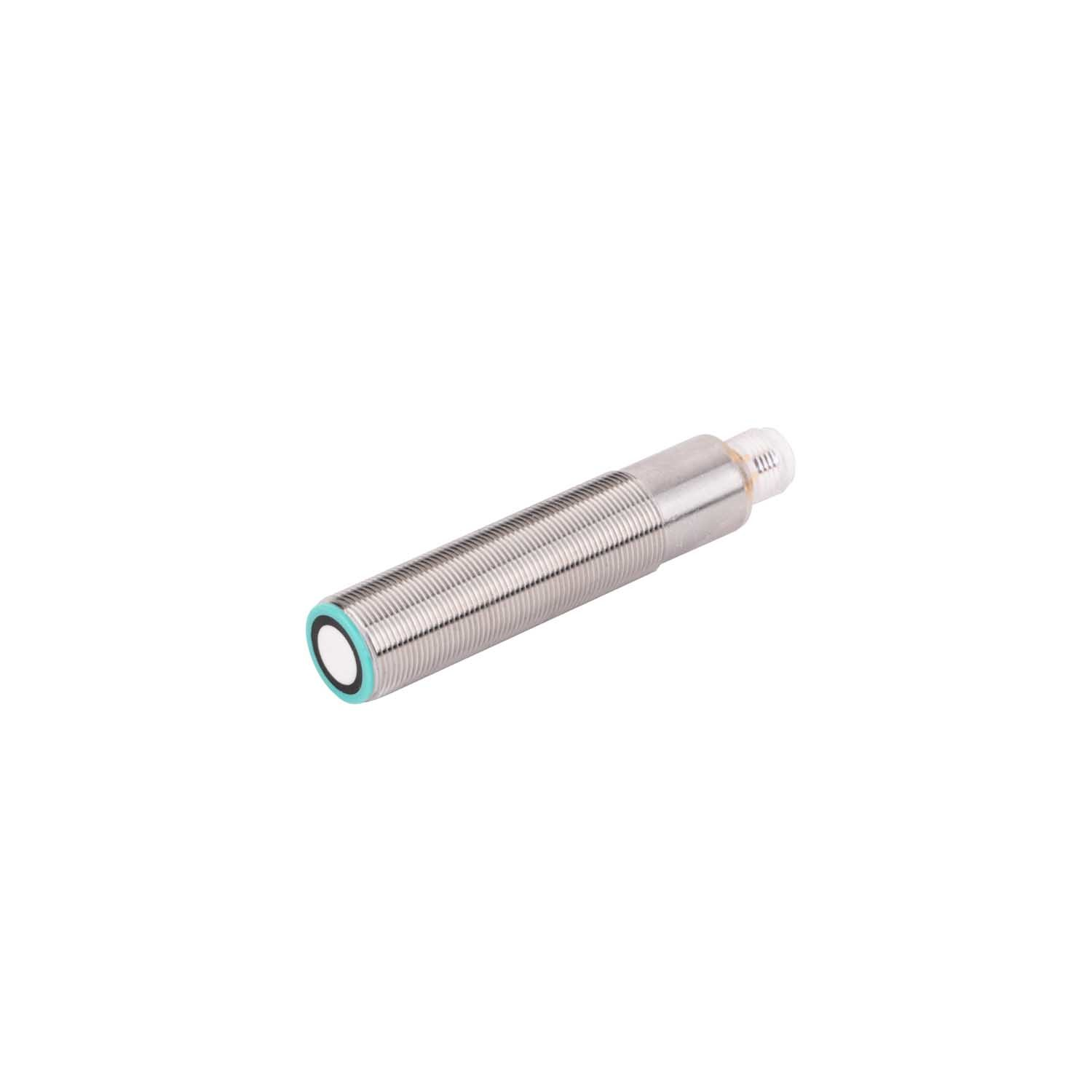
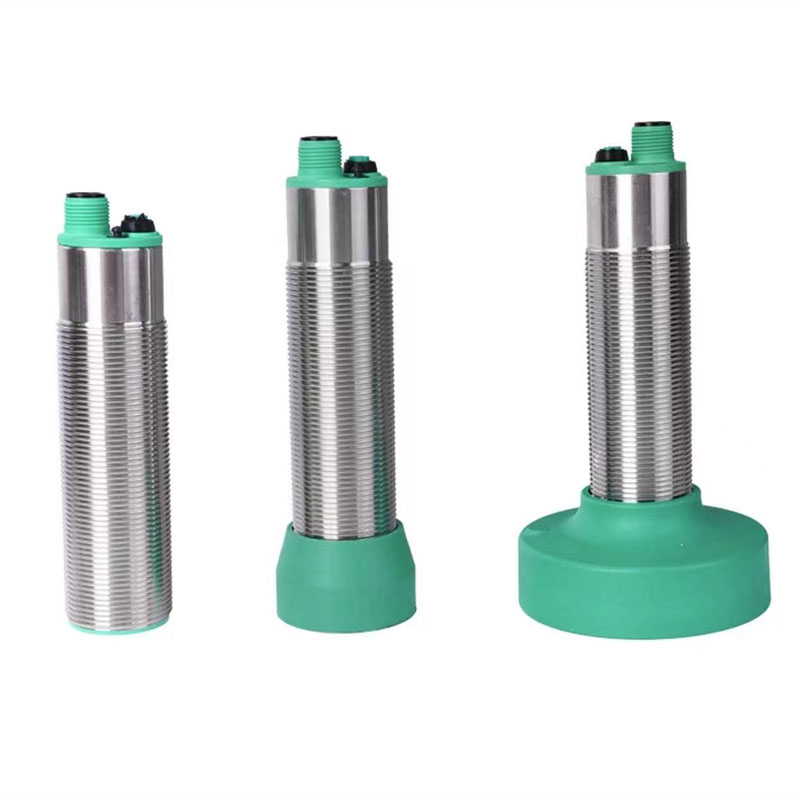
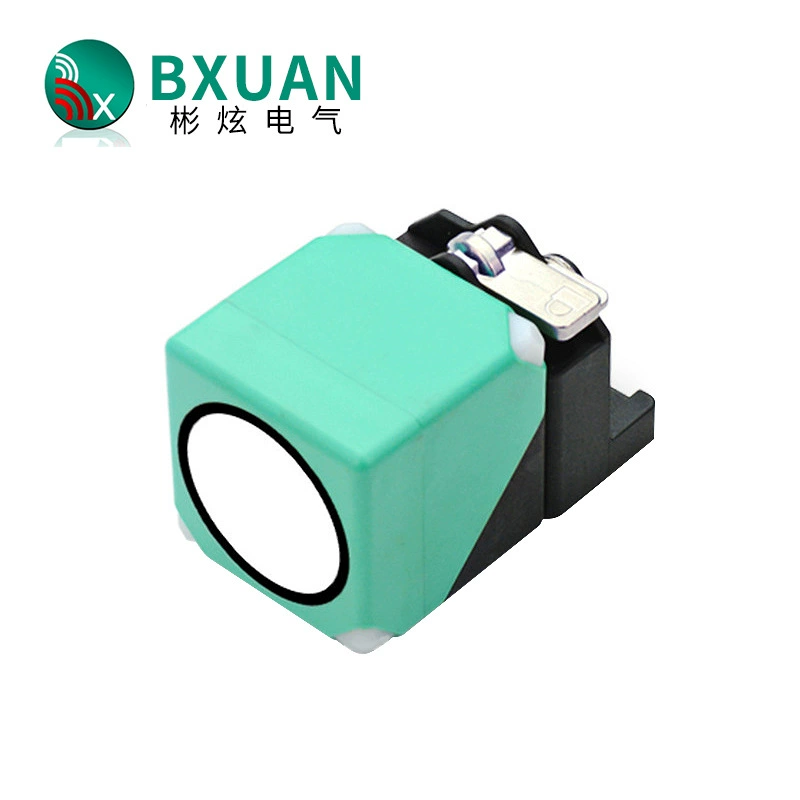
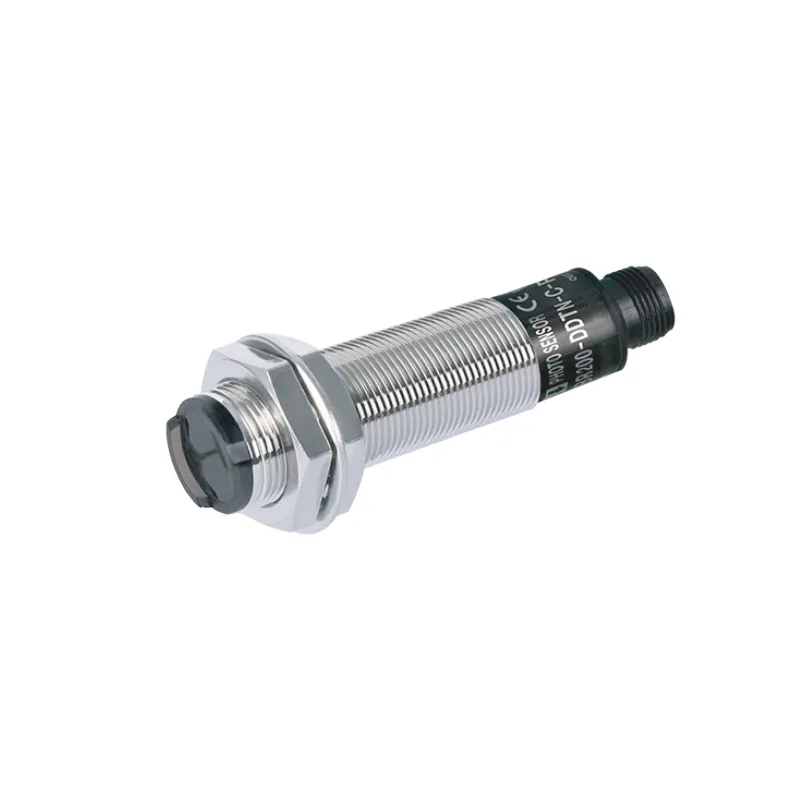
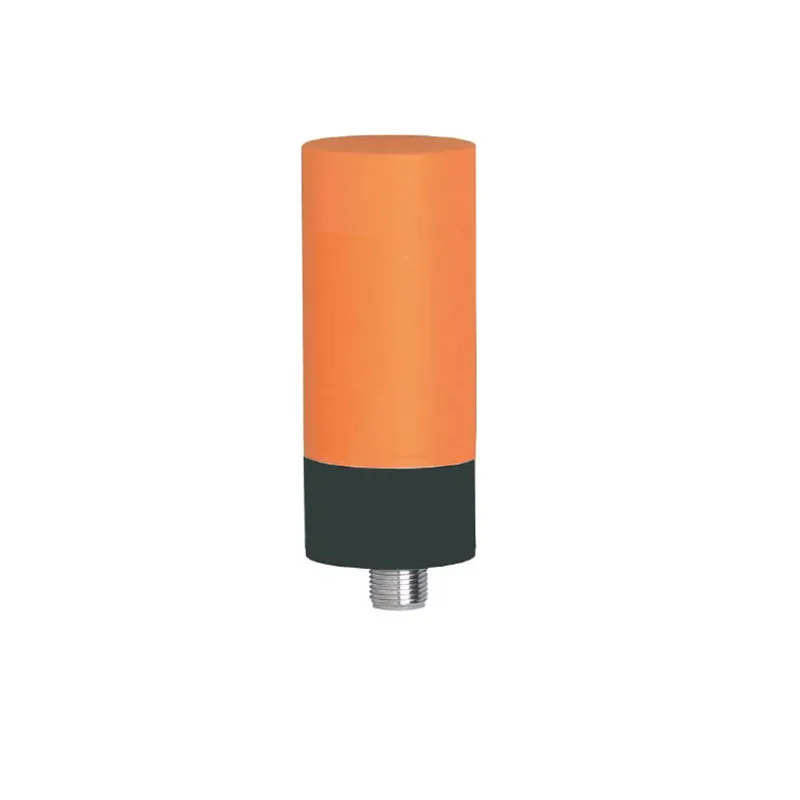
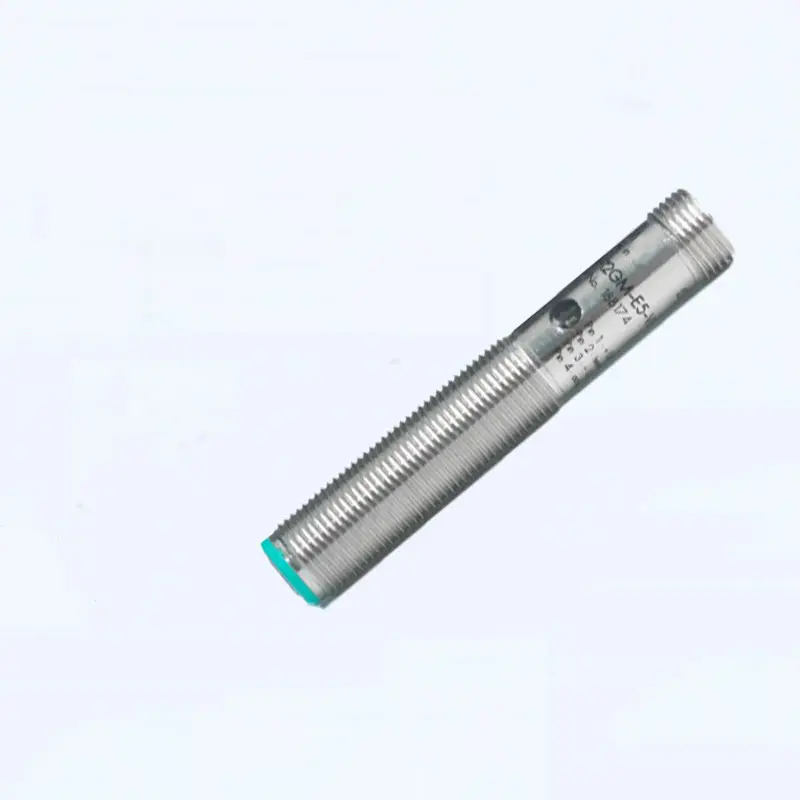
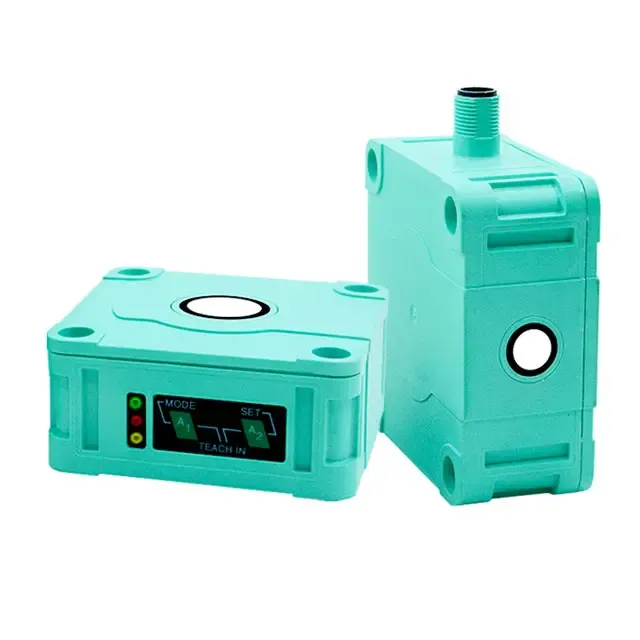
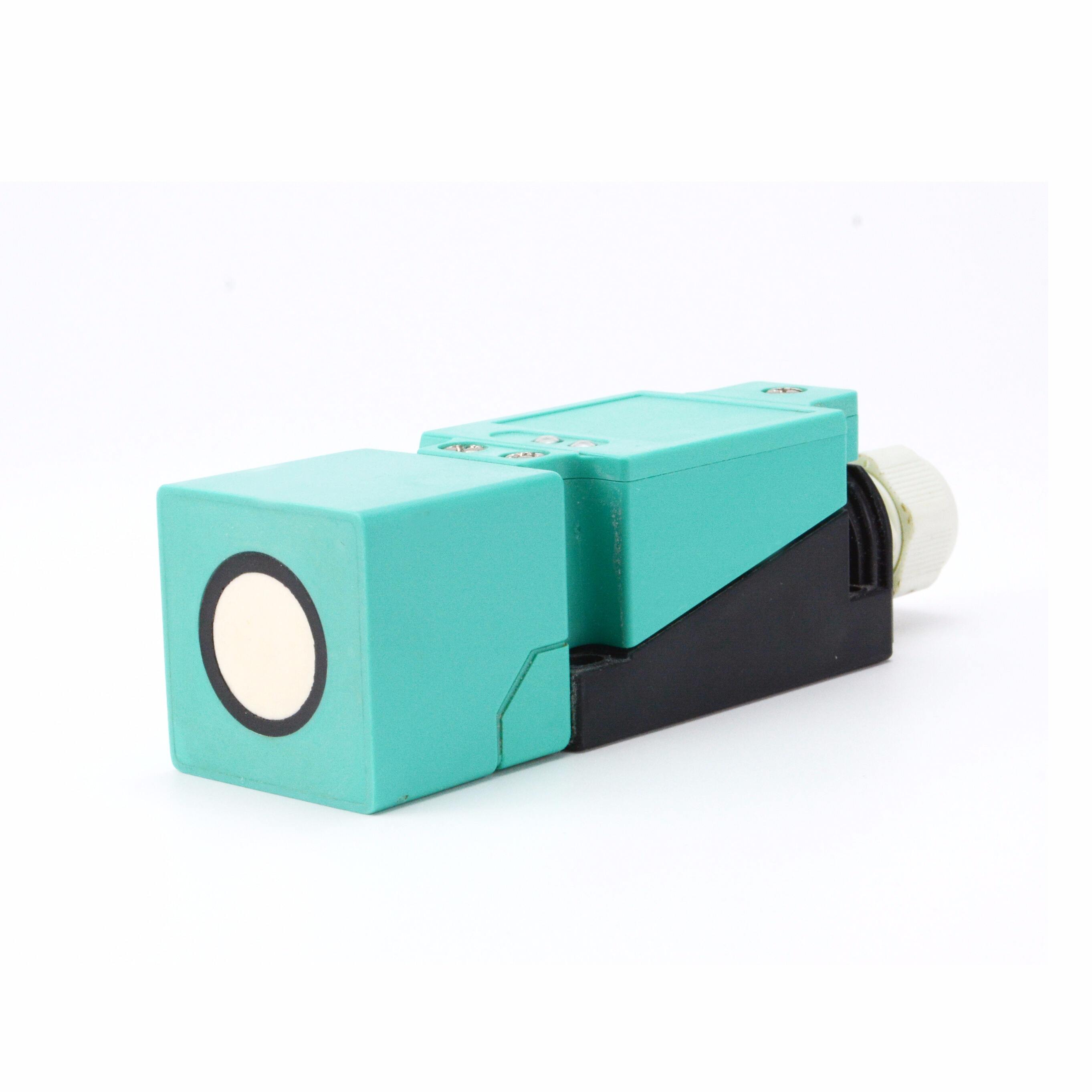
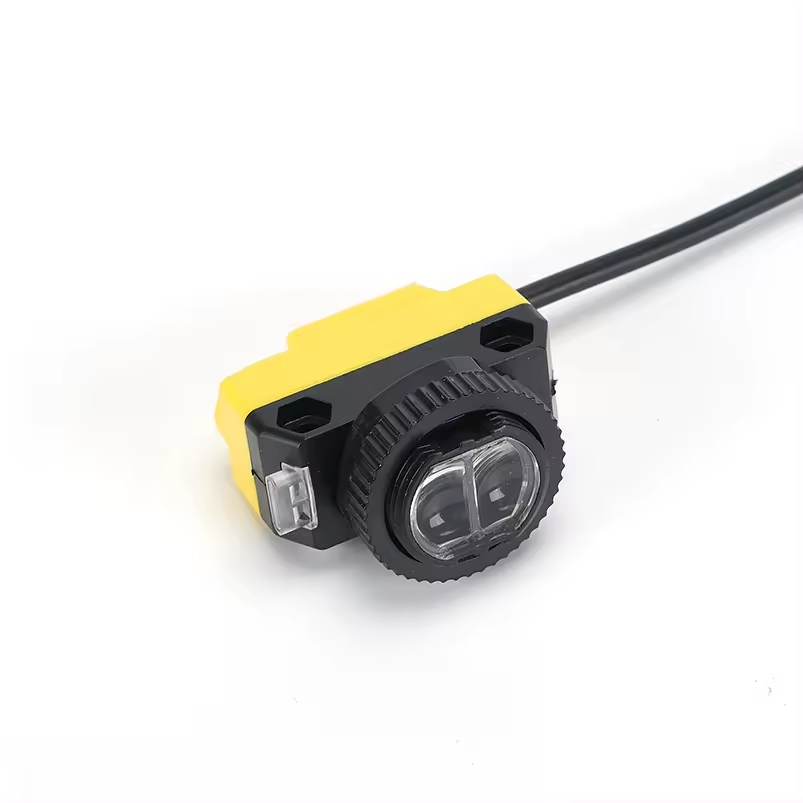
Ylivoimainen ympäristösopeutuvuus
Äänilähetimet osoittavat erinomaista suorituskykyä monenlaisten ympäristöolojen keskellä, mikä erottaa ne tavanomaisista tunnistusteknologioista. Niiden kyky toimia tehokkaasti haastavissa olosuhteissa, kuten pölyisissä, kosteissa tai huonosti valaistuissa tiloissa, tekee niistä arvokkaita teollisuussovelluksissa. Anturit säilyttävät tarkan mittaustarkkuuden riippumatta ympäristön valaistustasosta, toisin kuin optiset anturit, jotka voivat vaikeuksia pimeydessä tai kirkkaassa valossa. Niiden kestävyys ympäristötekijöitä vastaan, kuten lämpötilan vaihtelut ja ilmanpaineen muutokset, takaa tasaisen suorituskyvyn ulkoisissa sovelluksissa. Teknologian immuunisuus sähkömagneettiselle häiriölle mahdollistaa luotettavan toiminnan raskaiden koneiden tai sähkölaitteiden lähellä. Tämä ympäristöön sopeutuvuus poistaa tarpeen lisäsuojavarusteille tai erityisille asennusvaatimuksille, mikä vähentää kokonaisjärjestelmän monimutkaisuutta ja kustannuksia.