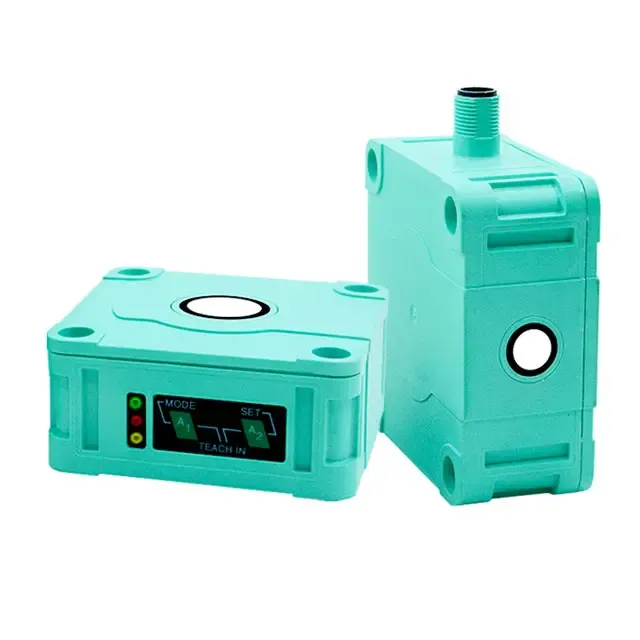
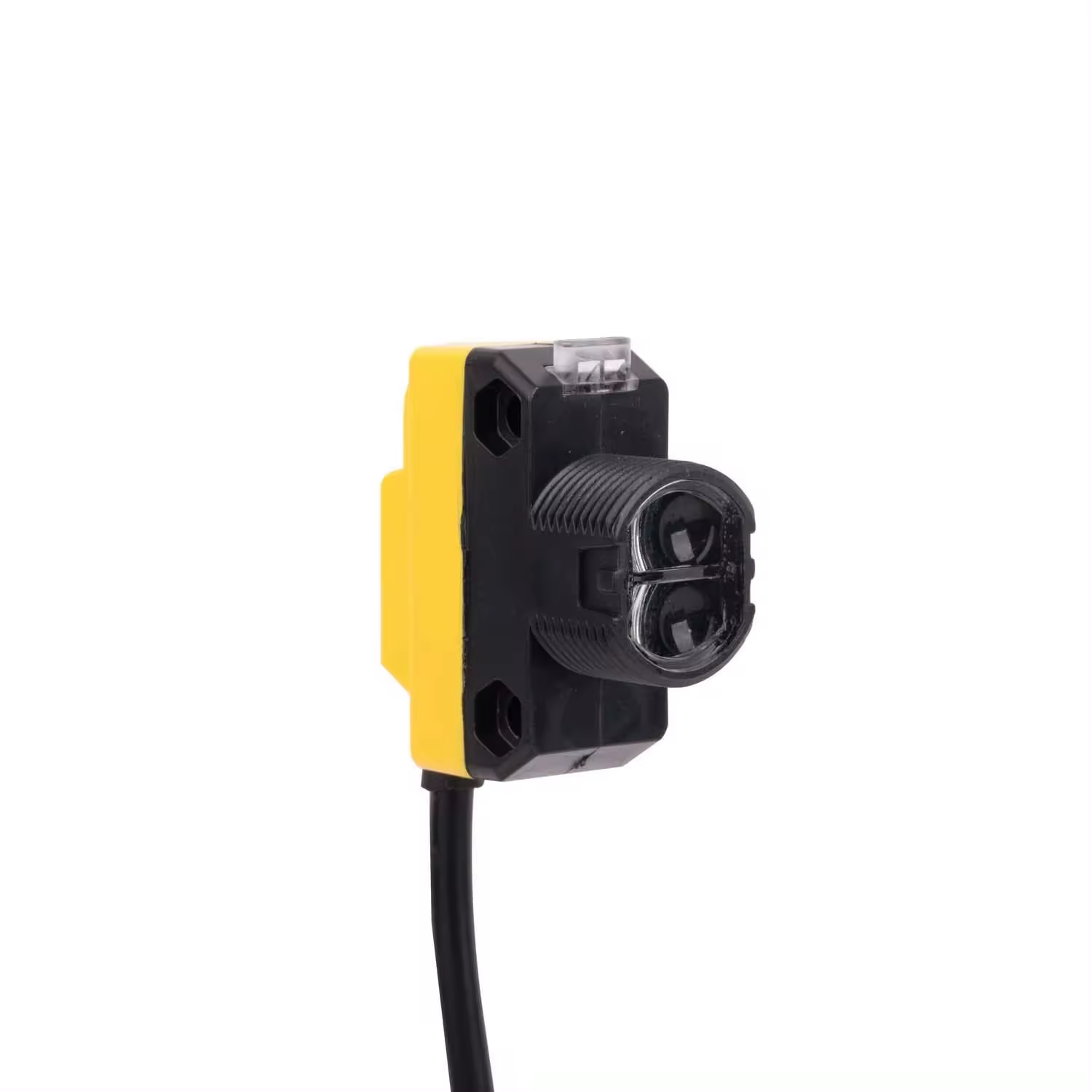
foto-sensorra lanera
Argi-sentsore bat, argi-elektriko-sentsore edo fotozelula gisa ere ezaguna, argi-intentsitatean gertatzen diren aldaketak detektatu eta erantzuten dituen osagai elektroniko aurreratua da. Bere funtzionamendu-printzipioa argi-energia argi-elektriko efektuen bidez seinale elektrikotan bihurtzean datza. Gailu hauek normalean argi-igortzaile bat izaten dute, LED edo laser bat adibidez, eta isladatutako edo eten den argi-izpiak jasotzen dituen jasotzaile bat. Argia gainazal argi-sentsibleari talka egiten zionean, elektroi-zulo bikoteak sortzen dira, argi-intentsitatearekin proportzionala den korronte elektrikoa sortuz. Argi-sentsore modernoek sentikortasun ajustagarria, iragazki digitala eta zeharkako-izpi, itzulirragazle eta difusio detekzio moduak barne hartzen dituzten ezaugarri aurreratuak dituzte. Ikusgaietatik infragoraino hedatzen diren argi-espektro desberdinetan lan egin dezakete, horrela aplikazio ezberdinetarako erabilgarriak izan dadin. Ingurune industrialean, objektuak detektatzeko, zenbatzeko, posizionatzeko eta kalitate-kontrolerako erabiltzen dira ohikoak dira. Lerro fabrikazio automatizatu, segurtasun-sistemak eta elektronika kontsumigarrien parte integrantea dira. Teknologia garatu egin da, autodiantsaia, tenperatura-konpentsazioa eta komunikazio protokolo digitalak bezalako ezaugarri adimentsuak barneratuz, ingurune zailenetan lan fidagarria ziurtatzeko.