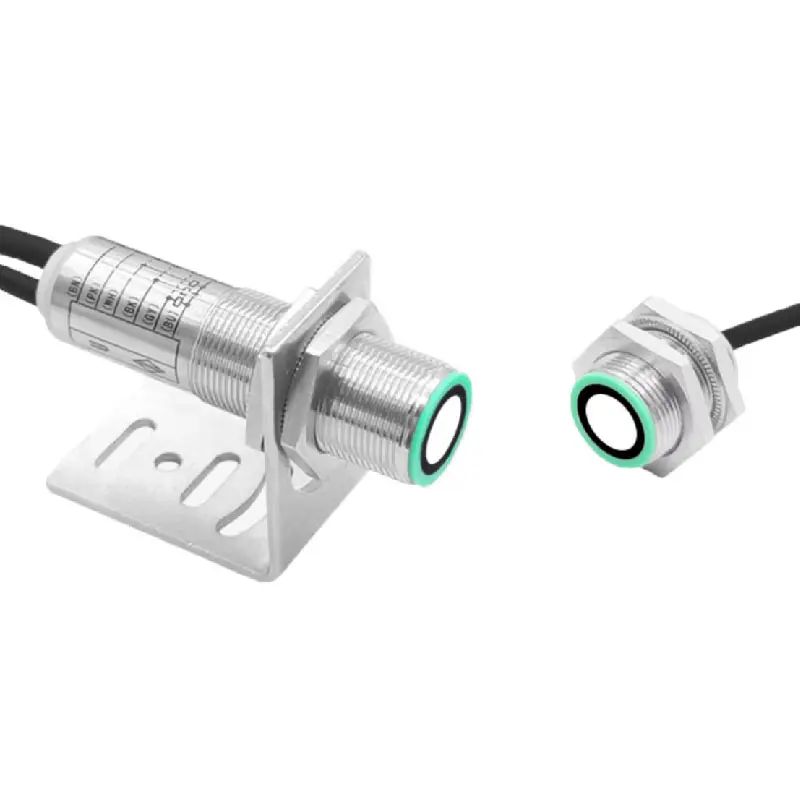
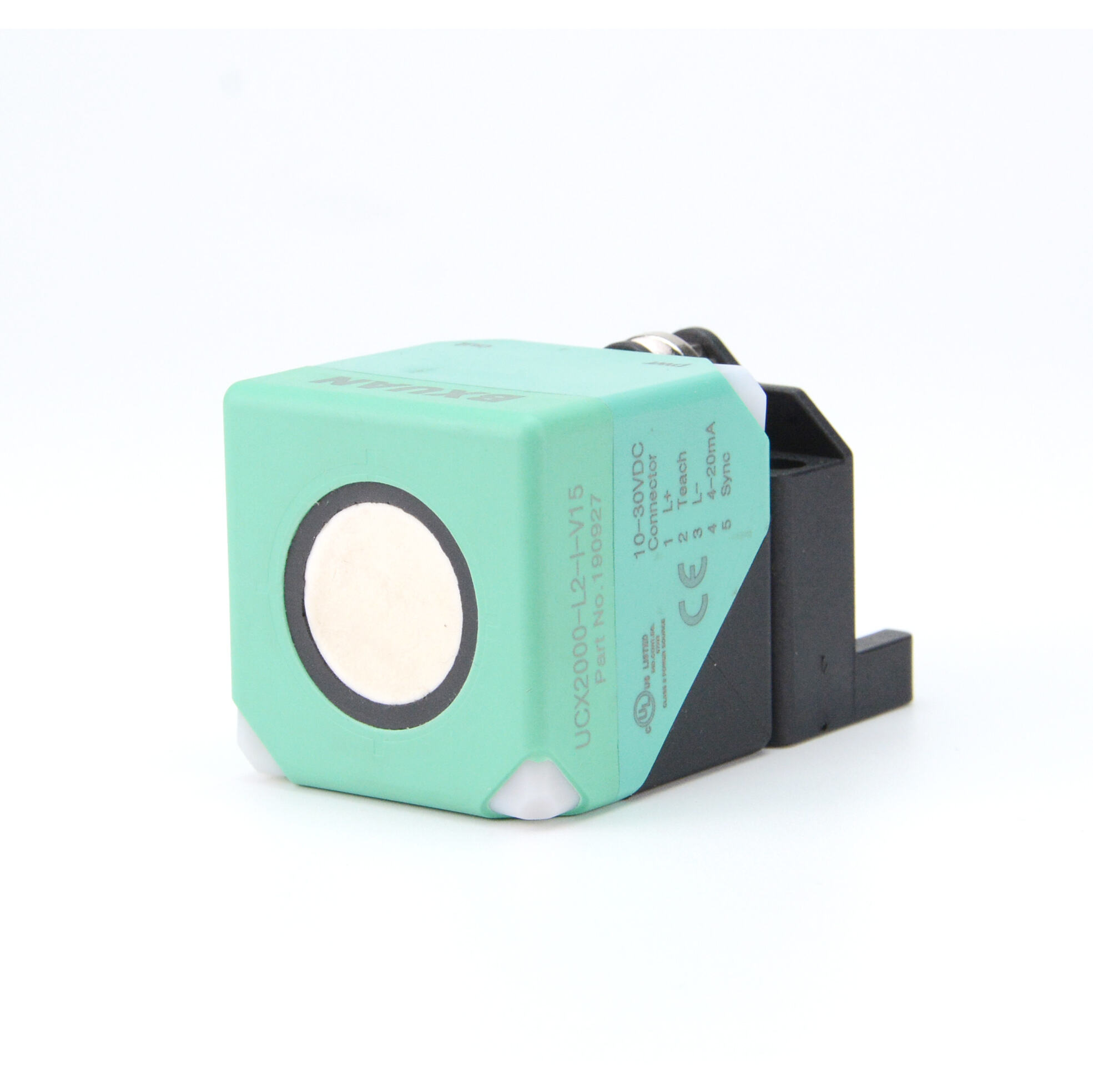
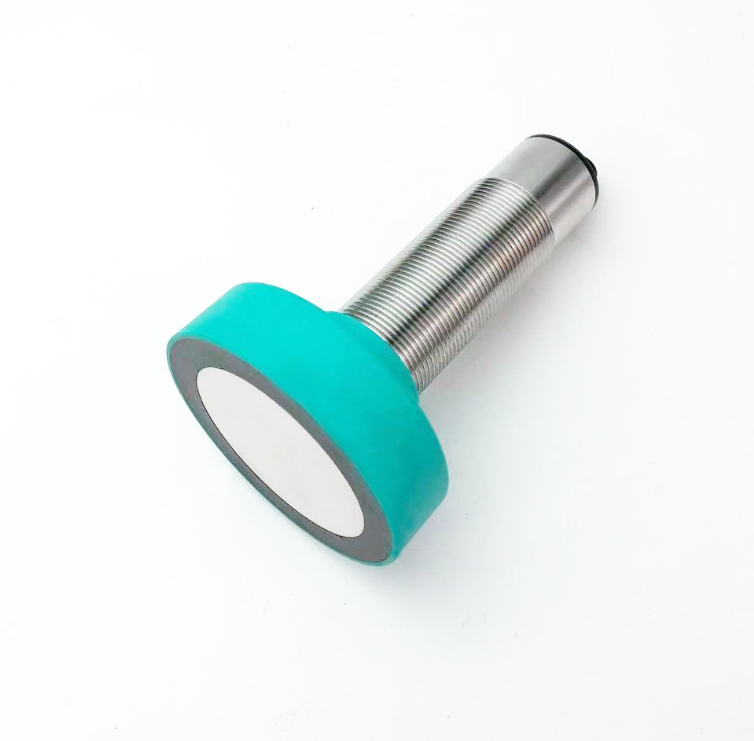
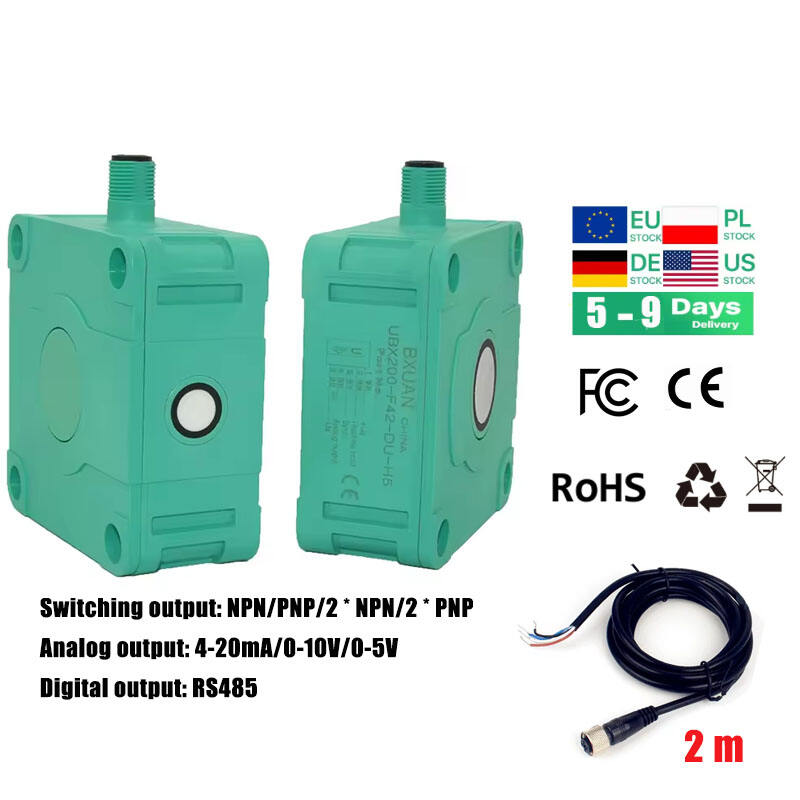
مستشعر فوق صوتي للتنقل في الروبوتات
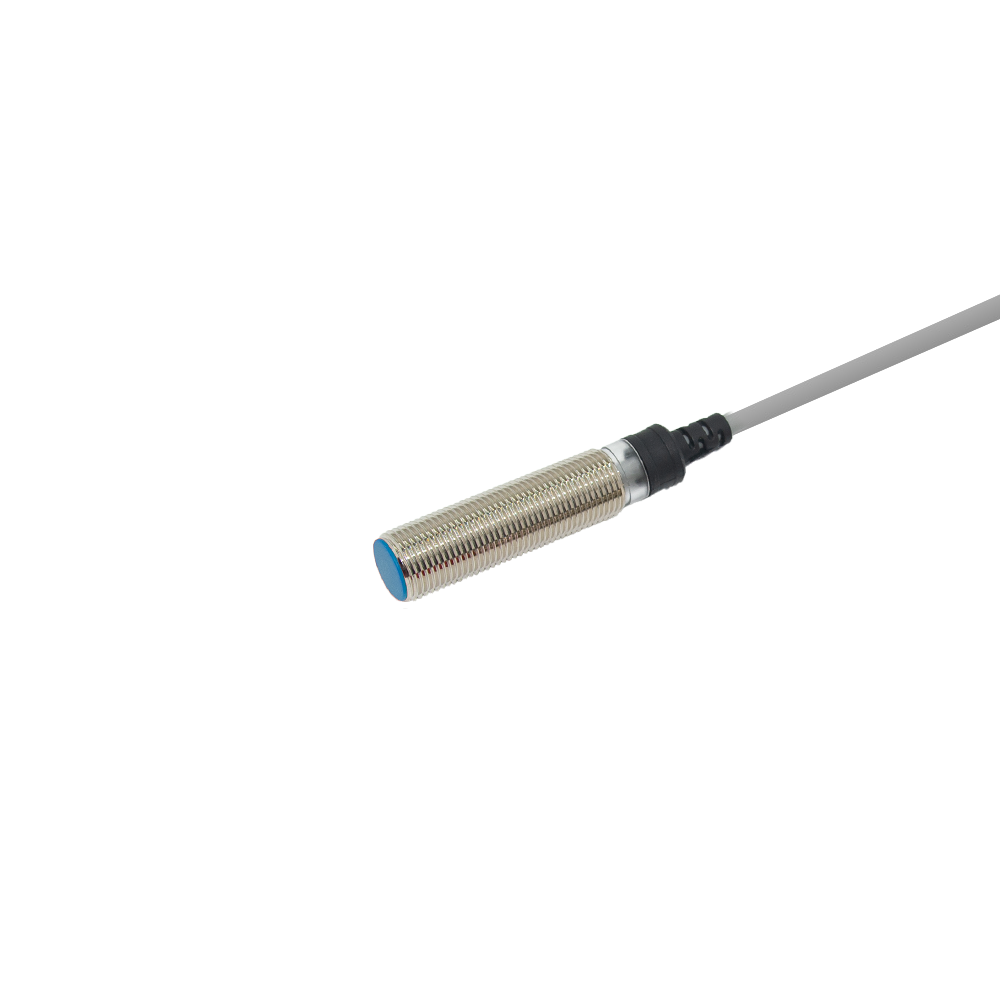
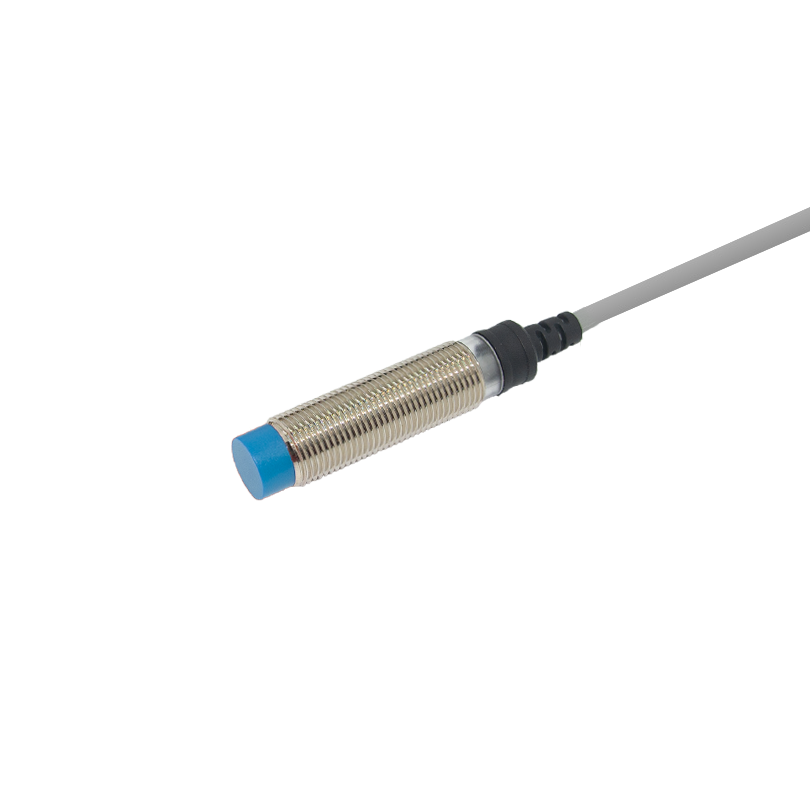
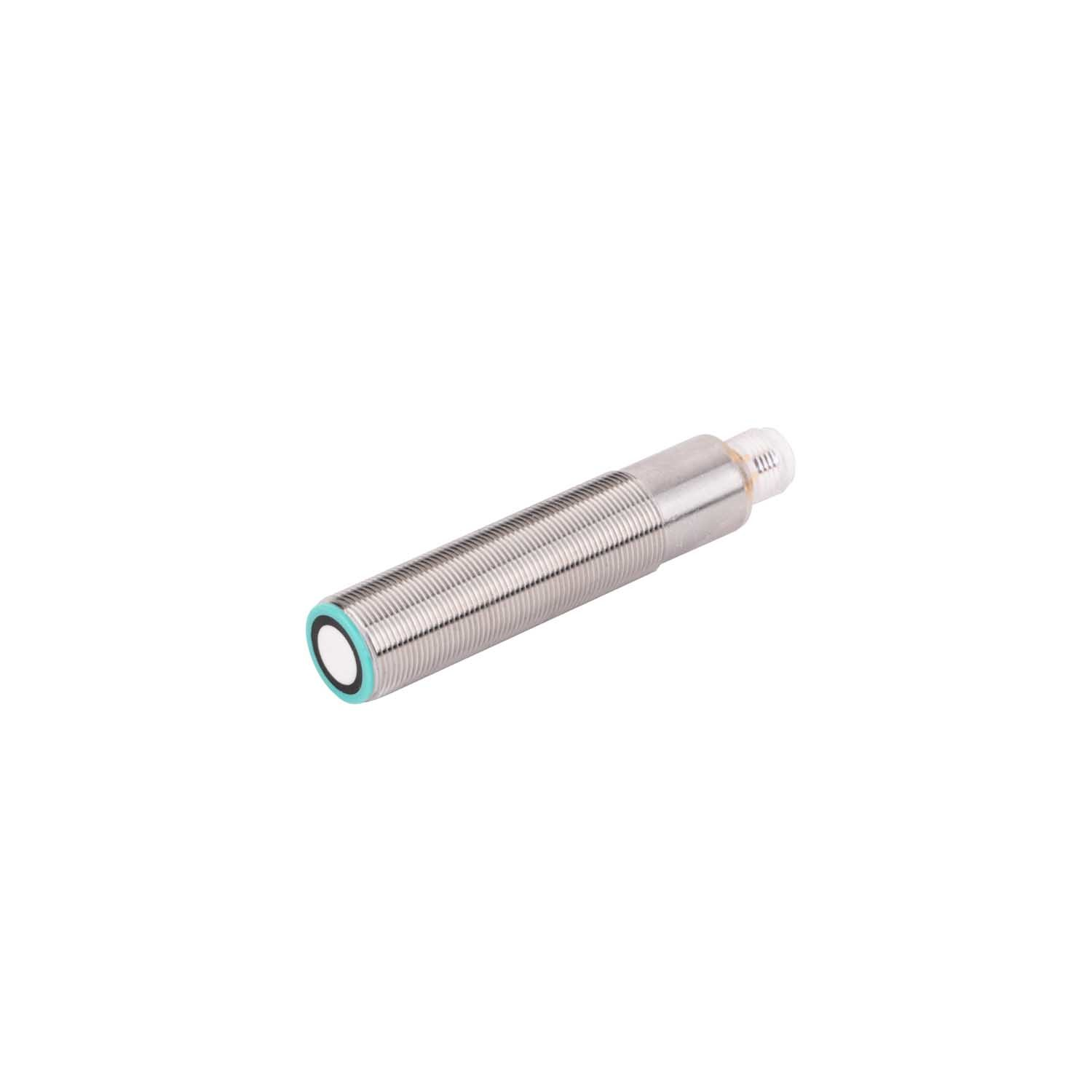
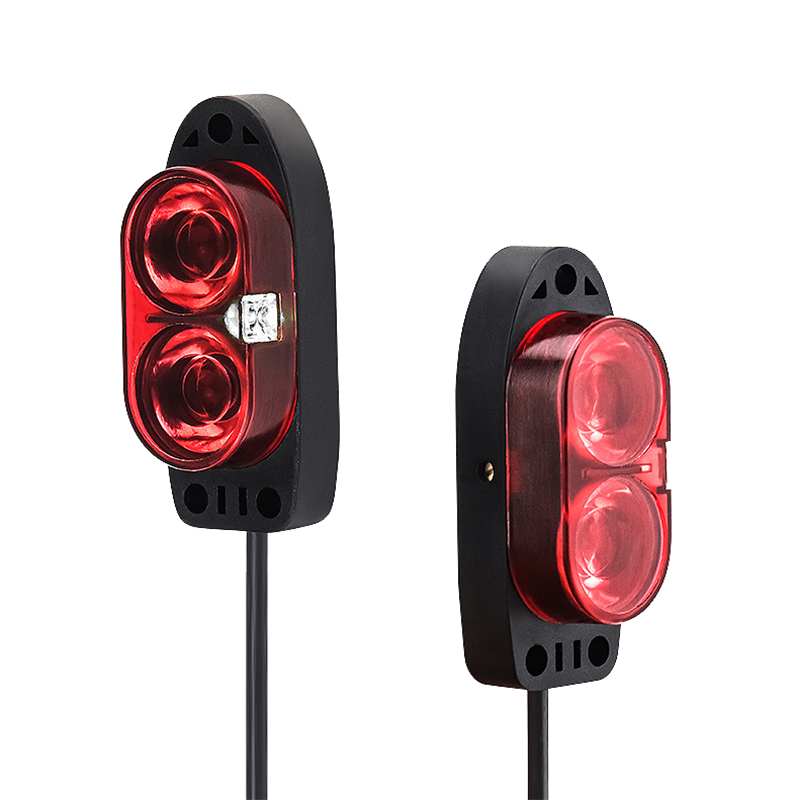
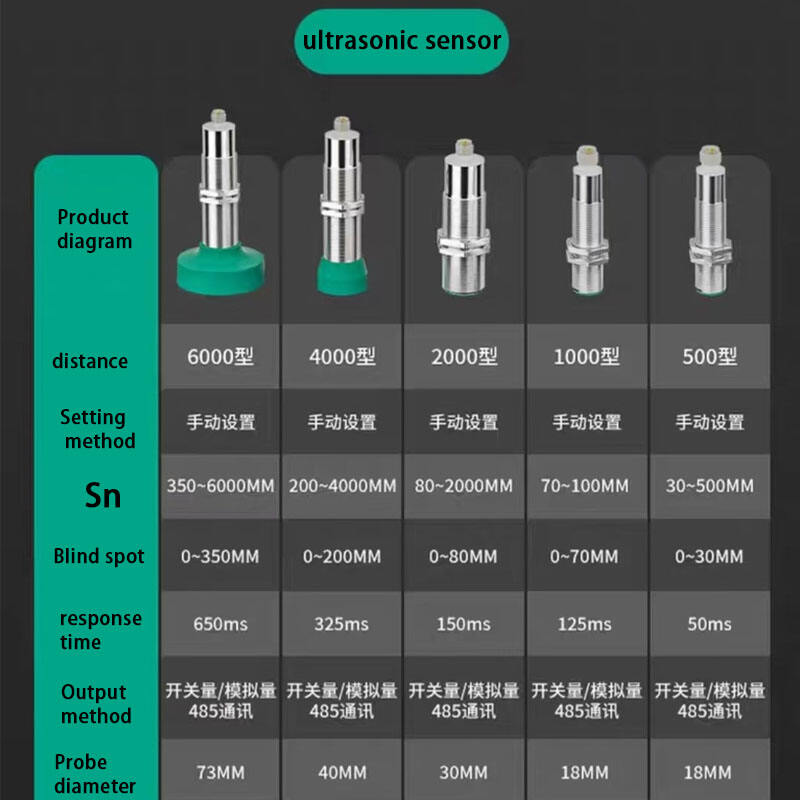
تمثل أجهزة الاستشعار فوق الصوتية للتنقل في الروبوتات تقدماً تكنولوجياً حاسماً في الأنظمة المستقلة، حيث تعمل كعيون وأذان الروبوتات الحديثة. هذه الأجهزة المتطورة تنبعث موجات صوتية عالية التردد وتقاس الوقت المستغرق لارتداد الموجات بعد اصطدامها بجسم، مما يوفر قياسات دقيقة للمسافات وقدرات على اكتشاف العوائق. يتكون نظام الاستشعار من جهاز إرسال ينتج الموجات فوق الصوتية، وجهاز استقبال يكتشف الموجات المنعكسة، ووحدات معالجة تقوم بتحويل هذه المعلومات إلى بيانات قابلة للاستخدام لأغراض التنقل. وتعمل هذه الأجهزة عند ترددات تفوق نطاق السمع البشري، وعادة ما تكون بين 20 كيلوهرتز و200 كيلوهرتز، وتتفوق في ظروف بيئية متنوعة، بما في ذلك الظروف ذات الإضاءة المنخفضة التي قد تواجه فيها أجهزة الاستشعار الضوئية صعوبات. كما توفر قياسات موثوقة للمسافات تتراوح من بضعة سنتيمترات إلى عدة أمتار، مما يجعلها مثالية للتطبيقات الروبوتية الداخلية والخارجية على حد سواء. وقد أثبتت هذه التكنولوجيا قيمتها الكبيرة في الأتمتة الصناعية والمركبات الذاتية القيادة وروبوتات الخدمة، حيث تعد القدرة الدقيقة على تجنب العوائق والوعي المكاني أمراً أساسياً للتشغيل الآمن والفعال. كما تضم أجهزة الاستشعار فوق الصوتية الحديثة ميزات متقدمة مثل تعويض درجة الحرارة، والتعرف على الانعكاسات المتعددة، وخوارزميات التصفية لتحسين الدقة والموثوقية في البيئات المعقدة.