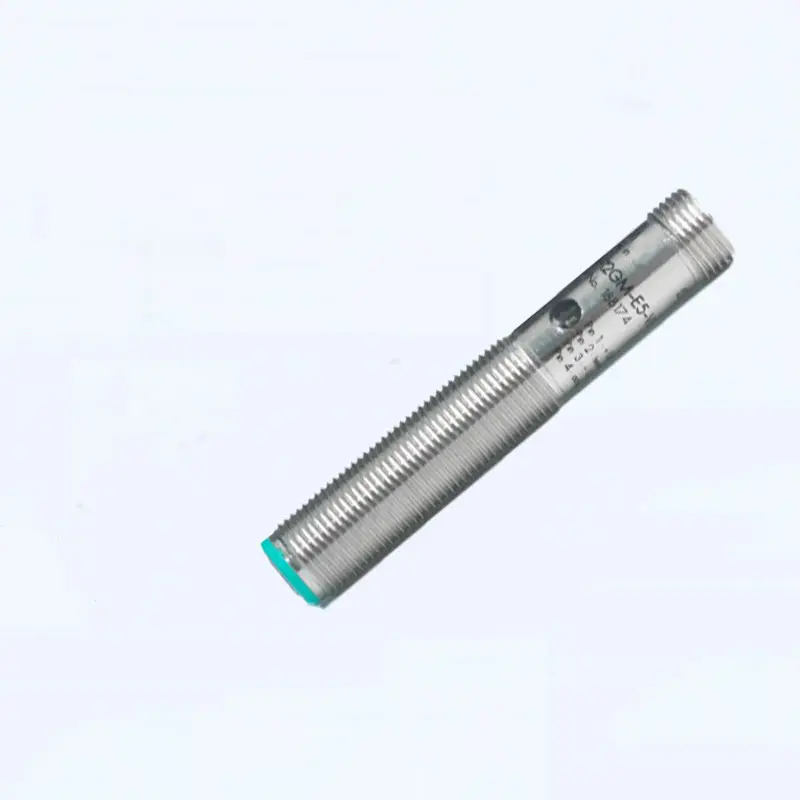
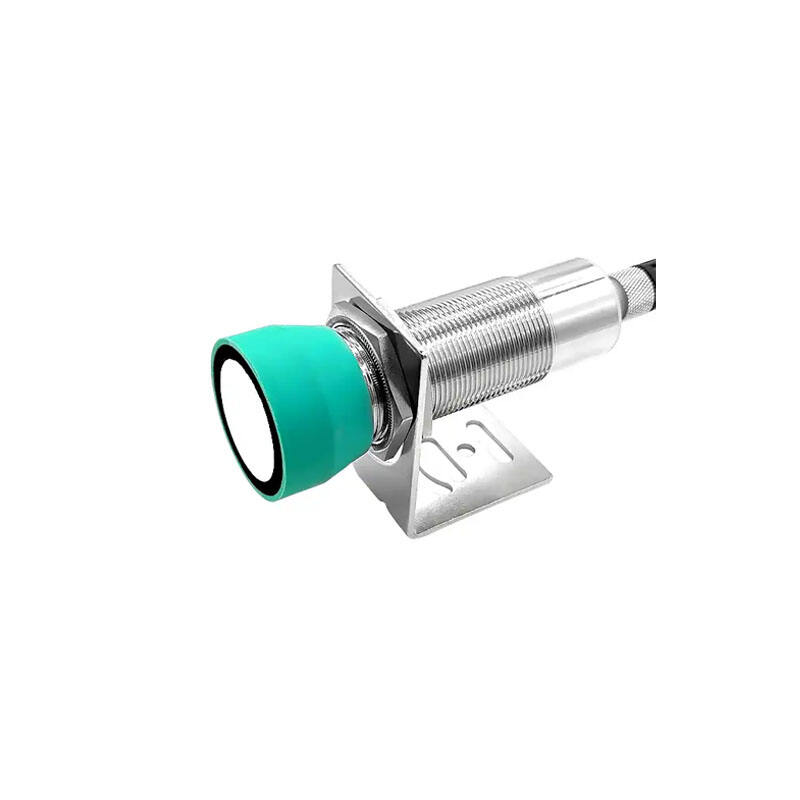
inductive proximity switch
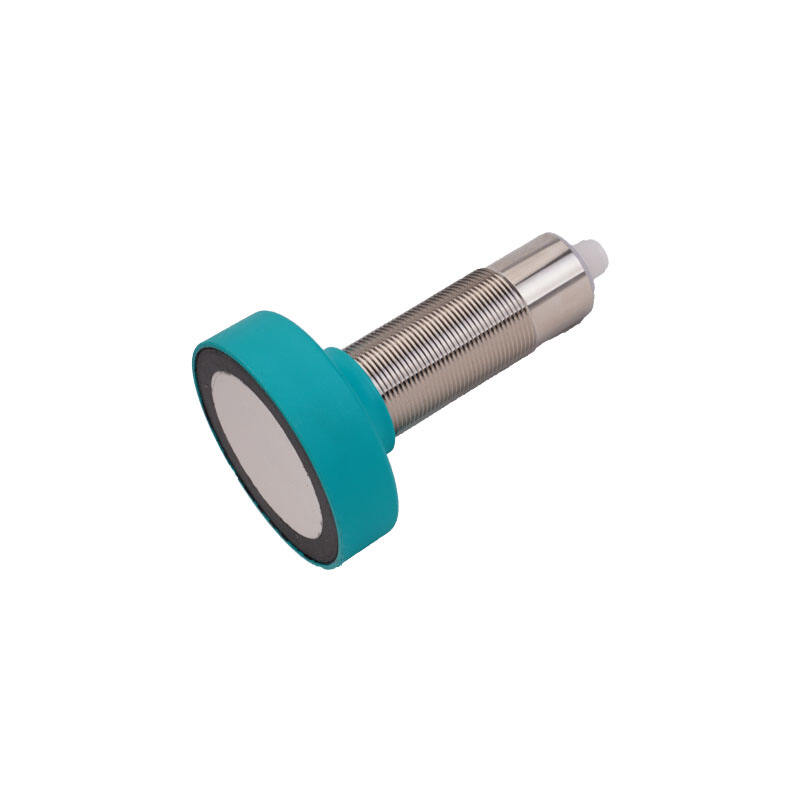
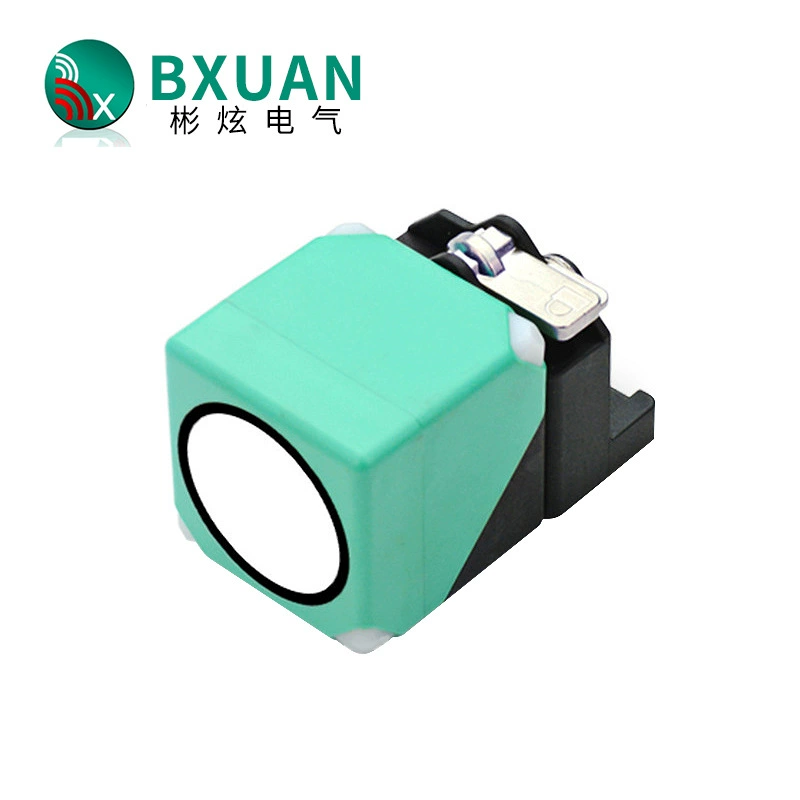
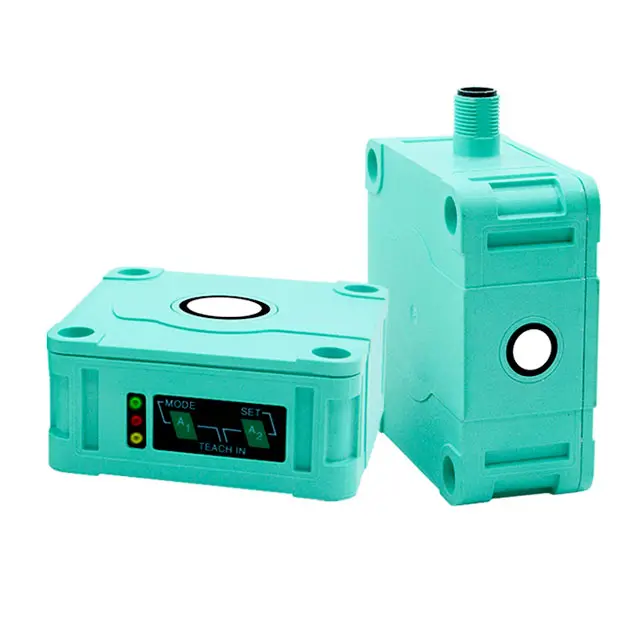
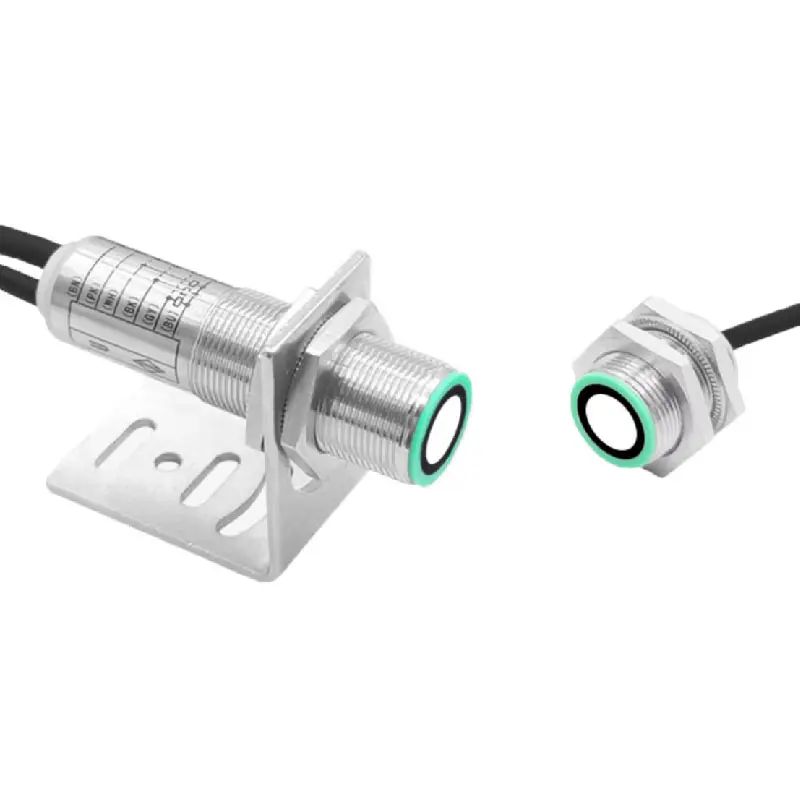
An inductive proximity switch is a sophisticated sensing device that revolutionizes automated detection in industrial applications. This non-contact sensor utilizes electromagnetic fields to detect metallic objects without physical interaction. Operating through an oscillator that generates a high-frequency electromagnetic field, the switch responds when a metallic target enters its detection zone, causing changes in the field strength. This technology enables precise and reliable object detection in various industrial environments. The switch consists of four main components: an oscillator, a detection circuit, an output circuit, and a protective housing. When a metal object approaches the sensing face, eddy currents are induced in the target, causing the oscillator's amplitude to change. This change triggers the output circuit, providing a clear signal indicating object presence. Modern inductive proximity switches offer various detection ranges, typically from 1mm to 40mm, depending on the model and target material. They excel in harsh industrial environments due to their sealed construction, often meeting IP67 or higher protection ratings. These switches support different output configurations, including PNP, NPN, normally open, or normally closed, making them versatile for diverse control systems. Their ability to operate in extreme temperatures, resist chemical exposure, and maintain consistent performance despite vibration or electrical noise makes them indispensable in modern automation.